UV-curing adhesive is a popular adhesive used in various industries, from electronics to medical devices. This type of adhesive is known for its quick curing time and strong bond, making it a reliable choice for many applications. But what exactly is UV-curing adhesive, and what are its advantages and disadvantages?
Let’s dive into this peculiar topic and uncover the taste, health risks, and even unique uses of glue beyond its intended purpose.
UV-curing adhesive is a type of adhesive that uses ultraviolet light to cure or harden. The adhesive is applied to the desired surface, and when exposed to UV light, it quickly hardens, creating a strong bond.
This adhesive is commonly used in industries where fast curing time is essential, such as electronics and medical devices. However, there are also some drawbacks to using this type of adhesive, which we will explore in this article.
What is UV-curing adhesive?
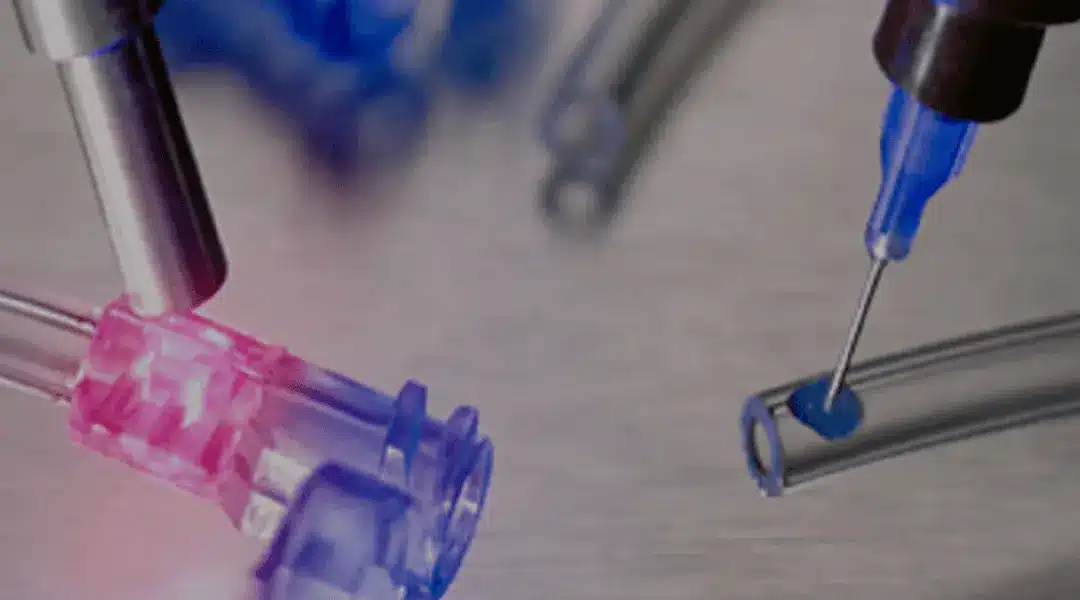
UV-curing adhesive, also known as UV adhesive or UV glue, is a type of adhesive that cures or hardens when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. Unlike traditional adhesives that rely on evaporation or chemical reactions to dry and form a bond, UV-curing adhesive requires the presence of UV light to initiate the curing process.
The adhesive remains in a liquid or semi-liquid state until it is exposed to UV light, which triggers a photochemical reaction, causing the adhesive to rapidly solidify and create a strong bond. This quick curing process makes UV-curing adhesive ideal for applications where fast assembly and bonding are required, such as in electronics, medical devices, optical instruments, and glass bonding.
Additionally, UV-curing adhesive offers excellent bonding strength and resistance to heat, chemicals, and moisture. Its ability to cure on-demand and in a controlled manner makes it a popular choice in various industries where precise and efficient bonding is essential.
Advantages of UV-Curing Adhesives
UV-curing adhesives offer a range of advantages and benefits that make them a popular choice for bonding applications. Let’s explore some of their key advantages:
Rapid Curing Times
One of the significant advantages of UV-curing adhesives is their rapid curing times. Unlike traditional adhesives that require hours or even days to cure, UV-curing adhesives can cure within seconds or minutes when exposed to UV light.
This quick curing capability makes them an ideal choice for high-speed production environments where time is of the essence. Manufacturers can significantly reduce production cycle times and increase overall productivity by using UV-curing adhesives.
High Bond Strength
UV-curing adhesives are known for their high bond strength. These adhesives can form strong, durable bonds between a wide range of materials, including glass, metal, plastics, and composites.
They are also capable of bonding dissimilar materials, which is often difficult or impossible with traditional adhesives. The strong bond strength provided by UV-curing adhesives ensures reliable and long-lasting adhesion, even in demanding applications.
Versatile Material Compatibility
UV-curing adhesives exhibit excellent compatibility with various materials. They can bond both porous and non-porous substrates, allowing for versatile application possibilities.
Whether it’s bonding plastics, metals, ceramics, or glass, UV-curing adhesives provide reliable adhesion on a wide range of surfaces. This versatility makes them suitable for diverse industries and applications, from electronics and automotive to medical devices and optical assemblies.
Environmental Friendliness
UV-curing adhesives offer environmental advantages over traditional adhesives. They do not require solvents or other chemicals for curing, reducing the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and minimizing environmental impact.
UV-curing adhesives are a greener alternative, aligning with sustainability goals and regulations. Their solvent-free nature also makes them safer to handle, minimizing health risks for workers and improving workplace safety.
Enhanced Process Control
UV-curing adhesives provide enhanced process control during bonding operations. Since the curing process is triggered by UV light exposure, there is no need to worry about adhesive flow or curing time variability due to ambient conditions.
Manufacturers can achieve precise control over the curing process, resulting in consistent bond quality and improved product reliability. The ability to control the curing process accurately contributes to increased process efficiency and reduced waste.
Improved Aesthetics
UV-curing adhesives offer excellent optical clarity and transparency. They leave no visible residue or adhesive lines, ensuring aesthetically pleasing bonding outcomes, especially in applications where aesthetics matter. This is particularly important in industries such as electronics and displays, where optical clarity and clean bonding are critical for optimal performance.
Uses of UV-Curing Adhesive
UV-cured adhesives have gained popularity in various industrial and commercial settings due to their versatility in bonding applications. They offer an effective solution for bonding a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, glass, and ceramics.
The rapid curing process under UV light enables quick and efficient bonding without the need for additional heat or solvents, making them an attractive choice for many manufacturing processes.
Rapid Curing with UV Light
One of the key advantages of UV-cured adhesives is their rapid curing time. When exposed to UV light, these adhesives polymerize and harden quickly, often within seconds or minutes.
This fast-curing capability is particularly beneficial in industries where high-speed production is essential. Manufacturers can achieve significant time savings and increase production efficiency by utilizing UV-cured adhesives.
Wide Material Compatibility
UV-cured adhesives exhibit excellent compatibility with various materials, enabling bonding between diverse substrates. Whether it’s bonding plastics to metals or glass to ceramics, UV-cured adhesives provide reliable adhesion on a broad spectrum of surfaces. This versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of industries, including electronics, automotive, aerospace, and medical devices.
Biocompatibility in Medical Devices
One major application of UV-cured adhesives is in the production of medical devices. These adhesives play a crucial role in bonding components in medical devices such as catheters, pacemakers, and surgical instruments.
The medical industry requires adhesives that are biocompatible, meaning they do not cause harm to the human body when used in medical applications. UV-cured adhesives are preferred in this industry due to their biocompatibility and low toxicity.
Bonding Dissimilar Materials
In the production of medical devices, it is common to use different types of materials in a single device. UV-cured adhesives excel in bonding dissimilar materials, allowing for the assembly of intricate medical components with various material compositions. This ability to bond different materials enhances the design and functionality of medical devices, promoting innovation and improving patient care.
Improving Safety and Reliability
The use of UV-cured adhesives in the medical industry has contributed to improved safety and reliability in medical devices. The strong and durable bonds formed by these adhesives ensure that the components remain securely attached, reducing the risk of device failure or malfunction.
Additionally, the biocompatible nature of UV-cured adhesives ensures that they do not adversely affect the body, enhancing patient safety during medical procedures.
Disadvantages of UV-Curing Adhesive
UV-curing adhesive, despite its numerous benefits, has certain disadvantages that may limit its use in certain applications. Let’s explore some of these drawbacks:
Sensitivity to UV Light
One significant disadvantage of UV-curing adhesive is its sensitivity to UV light. The curing process of UV-curing adhesive is initiated by exposure to UV radiation. While this rapid curing is advantageous in many applications, it can also be a disadvantage when the adhesive is exposed to UV light unintentionally or prematurely.
Exposure to other sources of UV light, such as sunlight or UV lamps used in light therapy, can trigger the curing process prematurely. This premature curing can lead to incomplete or improper bonding, compromising the strength and reliability of the adhesive joint. To avoid this issue, proper storage, handling, and protective measures should be employed to prevent incidental exposure to UV light.
Limited Bonding Strength
Another drawback of UV-curing adhesive is its limited bonding strength compared to some traditional adhesives. While UV-curing adhesives offer quick curing times and ease of use, they may not provide the same level of bonding strength required for high-stress applications.
In situations where exceptional bonding strength is critical, structural adhesives specifically designed for high-stress environments may be a more suitable choice. These adhesives are formulated to offer superior bonding performance and are commonly used in industries where strong and durable bonds are essential.
Curing Depth Limitation
UV-curing adhesives may have a limitation in their curing depth. The penetration depth of UV light may restrict the complete curing of thicker adhesive layers or materials with low UV transparency. This can result in inadequate bonding strength in certain joint configurations, particularly when bonding materials with significant thickness differences.
To address this limitation, proper adhesive selection and application techniques should be employed to ensure that the adhesive adequately cures throughout the entire bond line.
Equipment and Infrastructure Requirements
The successful application of UV-curing adhesive may require specialized UV light sources and infrastructure, which can add to the overall production cost. Manufacturers need to invest in suitable UV equipment to ensure proper curing and bonding performance.
Additionally, the need for UV light sources may necessitate adjustments to the production process, which can lead to increased complexity and may not be practical in certain environments.
Health and Safety Considerations
UV-curing adhesives, like other UV-curable materials, may raise health and safety concerns due to the use of UV light. Exposure to UV radiation can pose risks to human health, such as skin and eye irritation. Proper safety measures, such as the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and proper ventilation, are essential to ensure the safe handling and application of UV-curing adhesives.
How to Use UV-Curing Adhesive
UV-curing adhesive is a versatile and efficient bonding solution that offers rapid curing times and strong adhesion. Proper usage of UV-curing adhesive is essential to ensure successful bonding and optimal performance. Here are the steps to effectively use UV-curing adhesive:
1. Surface Preparation
Proper surface preparation is critical for achieving a strong and durable bond with UV-curing adhesive. Ensure that the surfaces to be bonded are clean, dry, and free from any contaminants, such as dust, grease, or oils. Thoroughly clean the surfaces using appropriate cleaning agents and techniques to promote adhesive adhesion.
2. Application of UV-Curing Adhesive
Apply the UV-curing adhesive to one or both of the surfaces to be bonded. The adhesive can be dispensed manually or through automated dispensing equipment, depending on the application requirements. Ensure the adhesive is evenly spread and covers the entire bonding area.
3. Aligning and Fixturing
After applying the adhesive, carefully align the components to be bonded to achieve the desired position. Use proper fixturing or clamping techniques to hold the components in place during the curing process. Proper alignment and fixturing are crucial to ensure accurate bonding and avoid any misalignment issues.
4. UV Light Exposure
Once the components are properly aligned and fixed, expose the adhesive to UV light. The UV light initiates the curing process, transforming the adhesive from a liquid or gel state into a solid bond. Ensure that the entire bonding area is exposed to UV light to achieve full curing.
5. Curing Time
The curing time of UV-curing adhesive depends on factors such as the adhesive type, thickness, and UV light intensity. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommended curing times for the specific adhesive used. It is essential to avoid premature or insufficient curing, as it can impact the bond strength and overall performance.
6. Post-Curing (Optional)
Some UV-curing adhesives may require post-curing to achieve optimal bond strength and performance. Post-curing involves subjecting the bonded assembly to additional UV light exposure after the initial curing process. This step can enhance the adhesive’s properties, especially in demanding applications.
7. Quality Inspection
After curing, inspect the bonded assembly to ensure proper adhesion and bonding quality. Check for any defects, voids, or incomplete curing. Conduct any necessary quality tests to validate the strength and reliability of the bond.
8. Adhesive Handling and Storage
Proper handling and storage of UV-curing adhesive are essential to maintain its performance and shelf life. Store the adhesive in a cool, dark place away from UV light sources. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for storage temperature and conditions.
9. Safety Considerations
When using UV-curing adhesive, take appropriate safety measures to protect against potential health risks from UV light exposure. Wear protective equipment, such as gloves and safety glasses, and ensure adequate ventilation in the workspace.
Is UV-Curing Adhesive Right for Your Project?
Making the decision to utilize UV-curing adhesive as a bonding technique requires careful consideration of various factors. Here are key points to keep in mind:
Benefits of UV-Curing Adhesive:
- Faster Curing Time: UV-curing adhesive offers rapid curing, increasing production efficiency and reducing cycle times.
- Stronger Bond: UV-cured bonds can provide reliable and durable adhesion between a wide range of materials.
- Clean Application: UV-curing adhesive leaves no residue or mess, ensuring a clean and aesthetically pleasing finish.
- Environmentally Friendly: The absence of solvents and low VOC emissions make UV-curing adhesive a greener option.
Limitations and Risks:
- Higher Cost: UV-curing adhesives may have a higher upfront cost compared to traditional adhesives.
- Equipment Expenses: Specialized UV light sources and infrastructure may be required for proper curing.
- Limited Bonding Strength: UV-curing adhesive might not be suitable for high-stress applications that demand exceptional bonding strength.
- Sensitivity to UV Light: The adhesive can cure prematurely when exposed to UV light, affecting bonding performance.
Project-Specific Considerations:
- Material Compatibility: Assess if the adhesive effectively bonds the materials used in the project.
- Required Bond Strength: Determine if the UV-curing adhesive meets the project’s bonding strength requirements.
- Curing Environment: Consider if your project’s workspace can accommodate UV light exposure and proper curing conditions.
- Project Scale: Evaluate the efficiency and suitability of UV-curing adhesive for the project’s size and production volume.
- Post-Curing Needs: Determine if post-curing is necessary to optimize bond strength and properties.
- Cost Comparison: Compare the cost of UV-curing adhesive to alternative bonding options.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider if the adhesive’s performance will meet the project’s environmental requirements.
Thorough Assessment:
- Conduct thorough testing and evaluation of UV-curing adhesive in your specific application to gauge its performance.
- Consider feedback and experiences from professionals in your industry who have used UV-curing adhesives.
- Ensure your team is adequately trained in handling and using UV-curing adhesive safely and effectively.
- Seek guidance from adhesive manufacturers or technical experts to make informed decisions.
By taking into account the benefits, limitations, and specific requirements of your project, you can determine whether UV-curing adhesive aligns with your needs and is a suitable bonding solution.
Conclusion
UV-curing adhesive is a versatile bonding solution that utilizes ultraviolet light to achieve rapid curing and strong adhesion. Its uses span across various industries, including electronics, medical devices, automotive, and more. The pros of UV-curing adhesive include fast curing times, reliable bonding, and an eco-friendly application.
However, it also comes with cons, such as sensitivity to UV light and limited bonding strength in high-stress applications. When considering UV-curing adhesive for a project, a thorough assessment of its benefits and limitations is crucial. By understanding its capabilities and limitations, you can make an informed decision and harness its advantages for efficient and reliable bonding solutions.




