Electrical adhesive is a type of adhesive that is specifically designed to bond electrical components and materials. It is a crucial element in the manufacturing and maintenance of electronic devices, appliances, and machinery.
Electrical adhesive comes in different forms and compositions, such as conductive, non-conductive, and thermally conductive, and each type has a specific purpose and application.
The use of electrical adhesive has become increasingly important in the field of electronics and electrical engineering due to its ability to provide a secure and reliable bond between components. As electronic devices become more complex and smaller, the need for a strong adhesive that can withstand high temperatures, vibration, and moisture is essential.
In this article, we will explore the various types and uses of electrical adhesive, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of its use. We will also provide tips on how to use electrical adhesive safely and effectively.
What is Electrical Adhesive
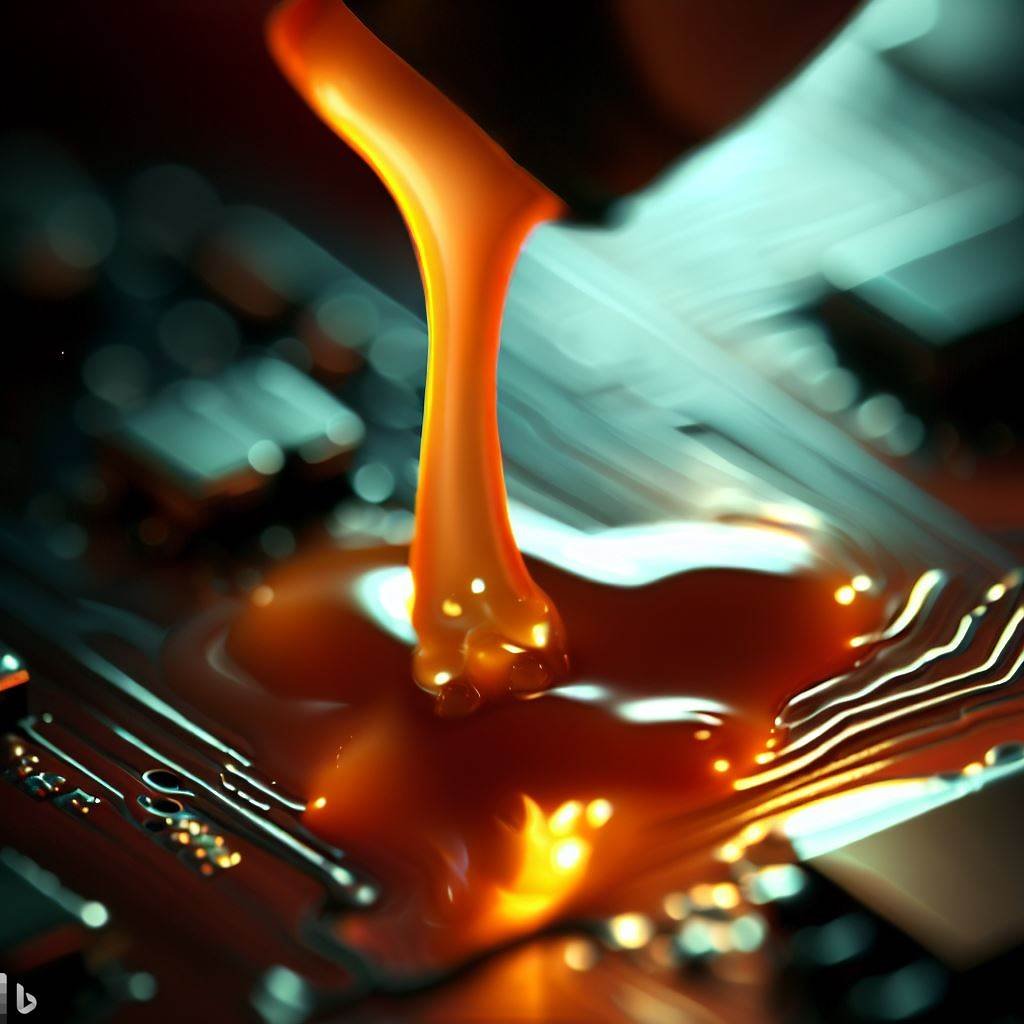

The application of an adhesive with conductive properties that securely bonds electrical components together is a crucial step in ensuring the reliability and safety of electronic devices. Electrical adhesive properties include excellent electrical conductivity, thermal stability, resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and chemicals, and high bonding strength and durability.
There are different types of electrical adhesives, such as epoxies, acrylics, and silicones, each with unique characteristics and applications. Epoxies are known for their high strength and chemical resistance, making them ideal for bonding metals and ceramics. Acrylics are known for their fast curing time and excellent adhesion to plastics, while silicones are known for their flexibility and resistance to extreme temperatures.
The bonding strength and durability of electrical adhesives are crucial factors in their application, as they need to withstand harsh conditions and mechanical stress. In the following section, we will explore the uses of electrical adhesive in various industries.
Uses of Electrical Adhesive
One might be surprised by the diverse range of applications that can be serviced by a substance that connects and secures materials together. Electrical adhesive is a type of adhesive that is specifically designed to be used in electrical applications.
In addition to its bonding strength, which is often stronger than traditional adhesives, electrical adhesive also has insulation properties that make it an excellent choice for use in electronic equipment, wiring, and other applications where electrical insulation is important. The adhesive is also resistant to heat and chemicals, making it suitable for use in harsh environments.
Electrical adhesive can be used to bond a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and ceramics. Its uses are not limited to the electrical industry, as it can also be used in the automotive, aerospace, and medical industries. The versatility of electrical adhesive makes it a popular choice for a wide range of applications.
With its excellent bonding strength and insulation properties, it is the adhesive of choice for many professionals in a variety of industries. Moving on to the advantages of electrical adhesive…
Advantages of Electrical Adhesive
The superior bonding strength and insulation properties of electrical adhesive make it a reliable choice for securing and protecting delicate electronic circuits and components, as well as various materials utilized in a broad range of industries.
Some advantages of using electrical adhesive include:
- Enhanced durability and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, heat, and chemicals.
- Faster curing times than traditional adhesives, allowing for quicker production and assembly processes.
- Improved aesthetics as the adhesive is often transparent and does not yellow over time.
- Decreased risk of damage to delicate components during application due to the precise and controlled dispensing.
While these benefits make electrical adhesive an effective choice for many applications, it is important to consider the potential downsides as well. The next section will explore some of the cons and provide an effectiveness assessment of electrical adhesive.
Disadvantages of Electrical Adhesive
This section delves into the limitations and drawbacks of utilizing electrical adhesive. According to a recent survey, approximately 30% of users reported difficulties with the adhesive’s dispensing and application process, which can be frustrating and time-consuming.
Additionally, electrical adhesive may not be suitable for certain applications due to its low tensile strength and limited resistance to high temperatures. In such cases, alternative bonding methods such as mechanical fastening or soldering may be more appropriate.
Despite these drawbacks, electrical adhesive remains a popular choice for many applications due to its ease of use, versatility, and ability to bond a variety of materials.
In the subsequent section about how to use electrical adhesive, we will discuss best practices and tips for achieving optimal results with this adhesive.
How to Use Electrical Adhesive
Exploring the proper techniques for utilizing a bonding agent in electrical applications can lead to improved outcomes and facilitate the attainment of a secure and long-lasting bond. Here are some essential techniques that can maximize the effectiveness of electrical adhesive:
- Surface preparation: Before applying the adhesive, it is crucial to clean the surface of the materials to be bonded. Any dirt, grease, or oil can weaken the bond and reduce its strength. The surface must be dry before applying the adhesive.
- Applying the adhesive: The adhesive should be applied in a thin and uniform layer using a brush or syringe. The amount of adhesive should be sufficient to cover the whole surface but not too much that it drips or creates lumps.
- Drying time: The drying time of the adhesive is crucial for the bond to form. It is recommended to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the drying time. If the adhesive is not allowed to dry completely, the bond may not be strong enough.
- Curing time: The adhesive should be allowed to cure for a specific time before subjecting it to any stress or load. The curing time varies depending on the type of adhesive and the materials being bonded.
By following these application techniques, the bond formed by the electrical adhesive can be strong and long-lasting. Safety precautions should also be taken into consideration when using electrical adhesive, which will be discussed in the subsequent section.
Safety Precautions
When using electrical adhesive, safety precautions are essential to ensure the well-being of individuals and the environment.
Protective gear such as gloves, goggles, and respirators should be worn to prevent skin and eye irritation and inhalation of harmful fumes.
Adequate ventilation is also necessary to avoid the accumulation of fumes in confined spaces.
Additionally, proper storage and disposal of adhesive containers and waste materials are crucial to prevent potential hazards.
Protective Gear
Appropriate protective gear is an essential consideration when working with substances that require caution, such as those used with electrical adhesive applications. Protective gear serves as a barrier between the skin and the potentially harmful chemicals found in the adhesive, reducing the risk of injury or exposure.
It is recommended to wear gloves, goggles or a face shield, and a respirator to protect against inhalation of fumes. Additionally, clothing that covers the entire body should be worn to prevent skin contact. It is important to note that not all protective gear is created equal, and the gear used should be specifically designed for the chemicals being handled.
While wearing protective gear is necessary, it is not a substitute for proper safety precautions. It is imperative to handle the adhesive with care and to follow all safety guidelines to minimize the risk of harm. With appropriate protective gear and safety precautions, working with electrical adhesive can be done safely and effectively.
Moving onto the subsequent section, proper ventilation is also crucial when working with electrical adhesive to ensure adequate air flow and reduce the risk of inhalation.
Proper Ventilation
Although it may seem counterintuitive, proper ventilation is often overlooked when working with certain substances, including those like electrical adhesive, that require caution and safety measures. It is essential to understand the importance of ventilation to ensure that the fumes and gases produced during the application of electrical adhesive do not affect your health.
Here are four factors that make ventilation a crucial aspect of working with electrical adhesive:
- Proper ventilation helps in maintaining a healthy airflow inside the workspace.
- It helps in regulating the direction of the airflow, ensuring that the fumes and gases move away from the user.
- Adequate ventilation prevents the buildup of hazardous substances in the air, which can cause respiratory issues, headaches, and dizziness.
- It also helps in reducing the risk of fire or explosion caused by the accumulation of flammable vapors.
Therefore, it is essential to use electrical adhesive in a properly ventilated area to avoid any health risks. With that said, proper storage and disposal of electrical adhesive is just as crucial, and we’ll explore that in the next section.
Storage and Disposal
Proper storage and disposal practices are crucial in ensuring the safe and responsible handling of substances commonly used in industrial applications, including electrical adhesive. Waste management is an important aspect of the storage and disposal process, as it helps prevent the release of potentially hazardous chemicals into the environment.
Electrical adhesive is often packaged in sealed containers that are labeled with information about the product, including its chemical composition and storage requirements. It is important to store electrical adhesive in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and sources of heat, as exposure to these elements can cause the adhesive to degrade and become less effective.
Additionally, electrical adhesive should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations and guidelines to minimize its environmental impact. This may involve transporting the adhesive to a licensed hazardous waste facility or working with a waste management company that specializes in the safe disposal of industrial chemicals.
By following proper storage and disposal procedures, businesses can help ensure the safe use of electrical adhesive while minimizing the potential impact on the environment.
Conclusion
Electrical adhesive is a type of bonding material specifically designed for use in electrical applications. It is used to join conductive components together, creating an electrical connection that is both strong and reliable. Electrical adhesive is commonly used in the manufacturing of electronic devices, such as computers, cellphones, and other gadgets that require a stable and secure electrical connection.
The advantages of electrical adhesive include its high tensile strength, durability, and resistance to high temperatures and chemicals. It is also easy to apply and can be used to bond a wide range of substrates. However, there are also some disadvantages, such as its relatively high cost and the fact that it can be difficult to remove once applied.
When using electrical adhesive, it is important to follow proper safety precautions, such as wearing protective gloves and eyewear and ensuring adequate ventilation in the workspace. Additionally, users should be aware of the potential hazards associated with the chemicals used in the adhesive and take appropriate measures to minimize their exposure.
In conclusion, electrical adhesive is a versatile and effective bonding material that is widely used in the electronics industry. While it has its advantages and disadvantages, proper use and caution can help ensure its safe and effective application. Like a dependable electrician, electrical adhesive holds the components of electronic devices together, creating a strong and reliable connection that powers the device.